
While native proteins still display their inter- and/or intra-chain bonds, creating secondary or tertiary structures, which may play a vital role in the activity of the protein, denatured proteins are most commonly used for Western blotting.
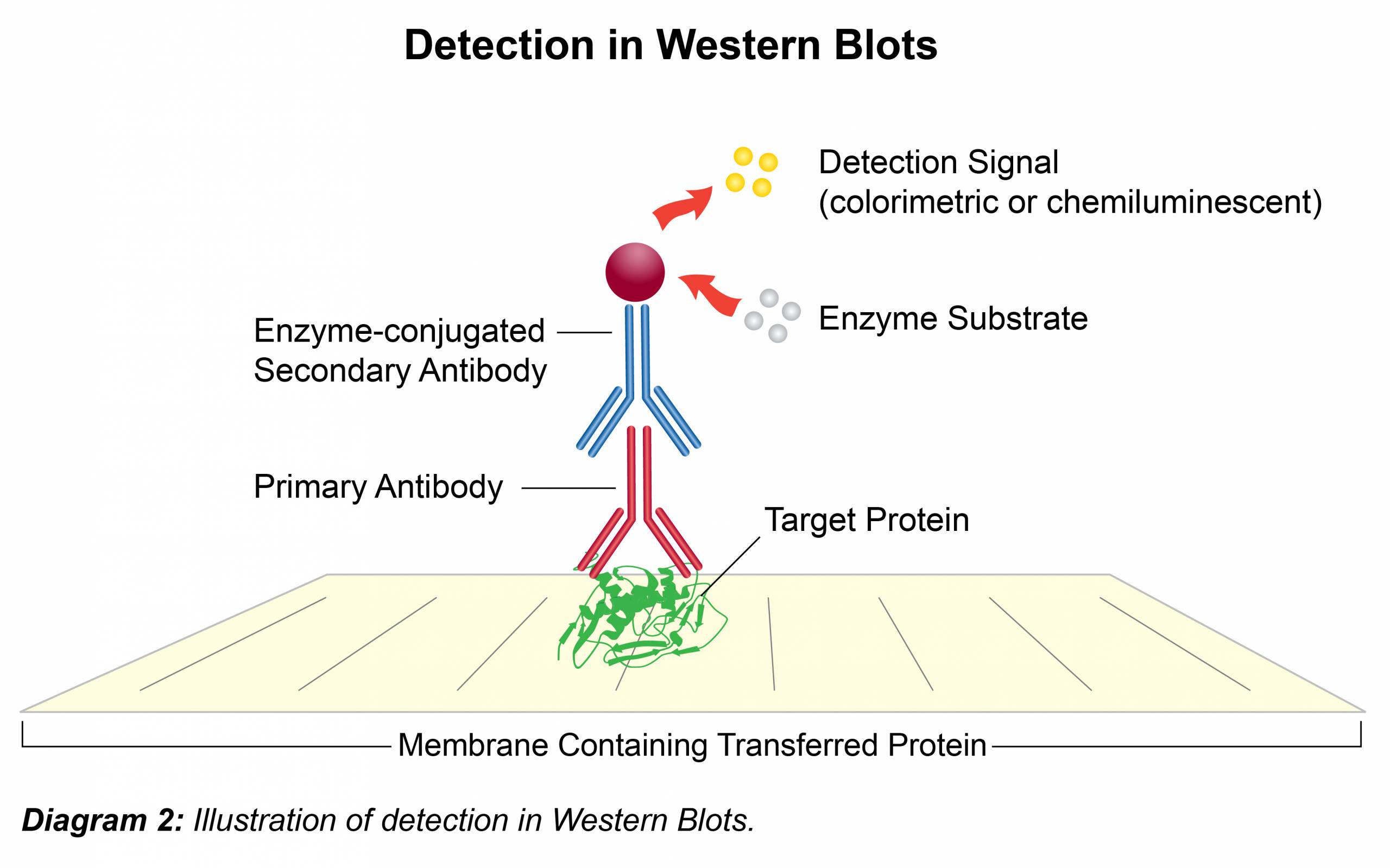
IEF separation may be accomplished by the addition of isophores to a polyacrylamide gel preparation, prior to crosslinking (casting gels), immobilization of pH gradients to a solid support (IPG strips), or using a solution phase technique. This pI may be variable for a given protein and indicative of the presence of post-translational modification such as sugars (glycosylation) or phosphates (phosphorylation). A protein reaches its pI when it has no net charge. IEF employs polyacrylamide gels containing a pH gradient, where a protein stops migrating under the influence of electric current at its isoelectric point (pI). The separation of native pr oteins relies on the sum of intrinsic char ges and is accomplished through isoelectric focusing (IEF). The proteins are loaded onto polyacrylamide gels (PAGE), three-dimensional mesh polymers composed of crosslinked acrylamide, which are thermo-stable, transparent, strong, and can be prepared with a wide range of average pore sizes. The electrophoresis separates proteins according to their electrophoretic mobility, when moving through a gel matrix under the influence of an electric field, depending on the charge, size and structure of the molecules. Bicinchoninic Acid Protein Assay, Coomassie Protein Assay) to ensure that equal amounts are loaded onto the gel. After protein extraction, the concentration of protein should be measured with commercially available protein concentration assays (e.g. It is important to avoid sample degradation at this point, which can be prevented by keeping the samples on ice and adding protease and/or phosphatase inhibitors. The first step in a Western Blot analysis involves the preparation of sample lysates for the subsequent protein separation. The analysis of protein migration and the intensity of either chromogenic, chemiluminescent or fluorescent signals offer protein expression details from cells or tissue homogenates. Typically, the primary antibody incubation is followed by a secondary antibody step, which is conjugated with a marker, used for signal visualisation.

SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) is used to separate proteins based on polypeptide length.įurther, the isolated proteins are transferred (blotted) onto a membrane matrix of nitrocellulose or Polyvinylidene Difluoride (PVDF), where they are detected with antibodies specific to target protein antigens. Western blotting is a protein detection method using specific antibodies and involves two major processes: separation of soluble proteins into distinct bands and the subsequent transfer of those proteins onto a solid matrix for subsequent analysis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
